Next: Subphrases as variation Up: Variation Module Previous: Lexicosemantic relationships Contents
Another important factor of lemon is the ability to model the differences between various words and forms of a word. This is performed by the properties lexicalVariant, formVariant and senseRelation. Again here we handle the large number of potential annotations by referring to a data category registry to define these relations.7
:hiv lemon:canonicalForm [ lemon:writtenRep "HIV"@en ] ; isocat:termType isocat:initialism ; isocat:initialismFor :human_immunodeficiency_virus . :human_immunodeficiency_virus lemon:canonicalForm [ lemon:writtenRep "Human immunodeficiency virus"@en ] ; isocat:termType isocat:fullForm ; isocat:fullFormFor :hiv . isocat:initialismFor rdfs:subPropertyOf lemon:lexicalVariant . isocat:fullFormFor rdfs:subPropertyOf lemon:lexicalVariant .
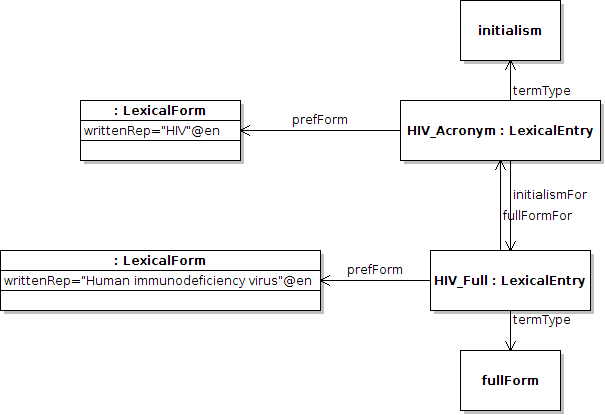
It is also possible to state lexical entries to be syntactic variants of another, if one is somehow derived from another. For example, the words “lexicon”, “lexical” and “lexicalize” are derived from a single root. This is done by means of the lexicalVariant relation. E.g.,
:lexicon :adjectivalVariant :lexical ; :verbalVariant :lexicalize . :adjectivalVariant rdfs:subPropertyOf lemon:lexicalVariant . :verbalVariant rdfs:subPropertyOf lemon:lexicalVariant .