lemon2gf is a Python script that transforms an ontology and one or more attached lemon lexica into a Grammatical Framework (GF) grammar.
lemon2gf can be downloaded from GitHub.
lemon2gf consists of two steps: mapping the ontology to an abstract syntax, and mapping a corresponding lexicon to a concrete syntax.
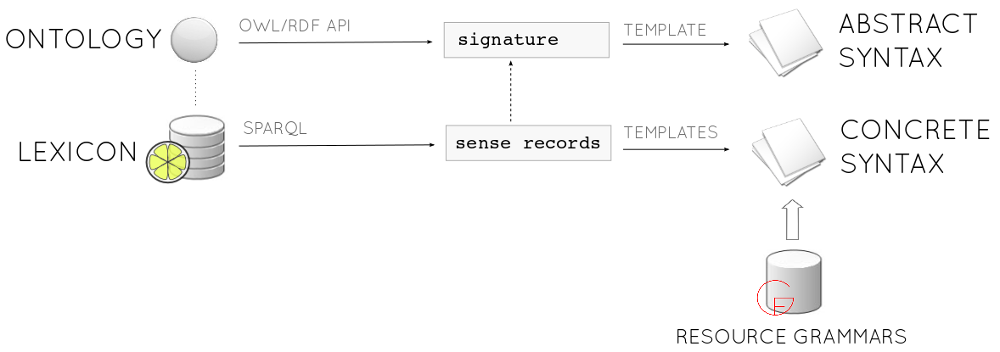
The generated GF grammar builds on a core that specifies the following categories:
cat
Class;
Individual Class;
Statement;In addition, it comprises domain-independent expressions and constructions, such as determiners, coordination and negation, that will not be provided in a domain lexicon.
Classes are mapped to constants of category Class,
e.g. the class dbpedia:Mountain becomes:
Mountain : Class;
Individuals are mapped to constants with their RDF type as type
parameter, e.g. resource:Nanga_Parbat becomes:
Nanga_Parbat : Individual Mountain;
Object properties are mapped to functions from individuals of the
domain type to individuals of the range type and have the return type
Statement, e.g. dbpedia:firstAscentPerson with
domain dbpedia:Mountain and range
dbpedia:Person becomes:
firstAscentPerson : Individual Mountain -> Individual Person -> Statement;
If a property does not specify a domain or range,
owl:Thing is assumed as default.
Datatypes are mapped to categories (keeping the prefix),
e.g. xsd:double becomes:
cat xsddouble;
Datatype properties are mapped to functions from individuals of
the domain type to the range category, again with return type
Statement, e.g. dbpedia:elevation with domain
dbpedia:Place and range xsd:double
becomes:
elevation : Individual Place -> xsddouble -> Statement;
Additionally, for each class a list of all superclasses are collected
and mapped to according GF judgements that allow for simple type
coercions, e.g. coercing Individual Mountain to
Individual Place.
First, all senses are collected. In case a sense does not refer to an
ontology URI, for example either refers to a URI defined in the lexicon
itself, or is composed of several subsenses, then the abstract syntax is
extended with according GF functions or constants. Currently, lemon2gf
covers the basic OWL constructs such as owl:unionOf,
owl:intersectionOf, owl:complementOf,
owl:propertyChainAxiom and owl:inverseOf.
Subsequently, for each sense all lexical entries denoting this sense are retrieved from the lexicon, together with all relevant morphosyntactic information. On the basis of its syntactic frame or, if no frame is specified, its part of speech, templates for GF linearization judgements are instantiated. For example, the following two lexical entries…
:mountain a lemon:LexicalEntry ;
lexinfo:partOfSpeech lexinfo:noun ;
lemon:canonicalForm [ lemon:writtenRep "mountain"@en ] ;
lemon:sense [ lemon:reference dbpedia:Mountain ] .
:peak a lemon:LexicalEntry ;
lexinfo:partOfSpeech lexinfo:noun ;
lemon:canonicalForm [ lemon:writtenRep "peak"@en ;
lexinfo:number lexinfo:singular ] ;
lemon:otherForm [ lemon:writtenRep "peaks"@en ;
lexinfo:number lexinfo:plural ];
lemon:sense [ lemon:reference dbpedia:Mountain ] .…are converted into the following linearization judgements:
lin Mountain = variants { mkCN mountain_N; mkCN peak_N };
oper
mountain_N = mkN "mountain";
peak_N = mkN "peak" "peaks";lemon2gf covers the most common LexInfo parts of speech and frames, and can be easily extended.